Operation
They are “Thermometers” that convert temperature into electric signals in order to be interpreted by on-board electronic systems.
Application
Used in vehicles with electronic fuel injection for the following measurements:
- Engine Coolant Temperature: measuring the liquid coolant temperature in engines cooled by water or the oil’s temperature in engines cooled by air.
- Fuel System Air Temperature: measuring the temperature of the inlet air.
- Ambient Air Temperature, inner and outer: In the electronic climatic systems, measuring the air temperature.
- Battery Temperature: In the integrated alternator control systems, measuring the battery temperature.
Operation Principle
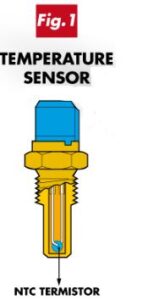
The main component used on Temperature Sensors for automotive systems are thermistors (NTC type resistors). These sensors are composed of a capsule or support, where the NTC element is assembled. (Fig.1). As shown in (Fig.2), the main feature of the thermistor (NTC: Negative Temperature Coefficient) is presenting an accentuated variation of its electric resistance in relation to its temperature.
Temperature increase -> resistance reduce
Temperature reduce -> resistance increase
The sensor assembly will depend on its use on the engine. When its purpose is to measure the engine coolant temperature, the NTC thermistor is located inside a protected capsule, isolating it from the liquid coolant.
For sensors destined to air temperature measurement (air cooling, outer/inner air), the NTC element remains exposed to airflow.
Note: The air change temperature sensor (ACT) can be associated with the manifold absolute pressure sensor (MAP) forming a combined sensor, which in some cases is identified as MAT
Location
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor: In the Thermostat housing, on the engine block or on the intake manifold base. in cases where the cooling fluid flows through it (engines powered by alcohol).
Air Change or Fuel System Temperature Sensor: In the intake manifold (multipoint systems) or in the cover of the throttle body (mono-point systems).
Use
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor – Used to:
- Adjust the fuel mixture: enriching mixture while the engine is cold.
- Adjust timing: This causes delays when the engine is hot in order to avoid detonation.
- Control the radiator’s fan.
Fuel System Air Temperature Sensor – Used to:
- Adjust the Ignition point.
- Calculate the admission’s cooling air mass in “speed/density” systems.
When it does not work
- Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor: Increases consumption. In early ignition systems can cause engine choke.
- Fuel System Air Temperature Sensor: Detonation; irregular idle speed, overheating.
Maintenance
Important actions when changing the temperature sensor:
- Avoid excessive tightening.
- Bleed the air (remove air bubbles) from the cooling system.
Diagnostic
For these Sensors there are three failure types:
-
- The sensor sends the wrong information but under the working range.
- The sensor sends the wrong information out of the working range (Sensor in short or open circuit).
- The information is wrong (short or open circuit) for some temperatures (intermittent failure).
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
In all cases, the diagnostic can be done with the use of test equipment (scanner tool) or voltmeter.
For case 1: Use mode “check working parameters” and compare it with the current engine’s temperature or inlet air temperature.
For case 2: Use mode “Read stored failures”.
For case 3: With the sensor connected and using a voltmeter, check the presence of tension peaks in the sensor’s signal measurement, while the engine warms from ambient temperature until proper working temperature. The sensor analysis (short or open circuit) is performed with the use of an ohmmeter. To check the calibration, in addition to the ohmmeter, it is crucial to have the current-voltage characteristic and the calibration specs supplied by the manufacturer.
Cares
- Always check the right temperature sensor for each vehicle model.
- Never perform maintenance repair while the cooling system is still hot. There is a high risk of burns.
- At any evidence of excessive temperature, park the vehicle in a safe place and turn off the engine immediately, otherwise, you may damage the engine.
- Check the coolant level weekly, with the cold engine.
- Always use the specified coolant and the correct rate for your vehicle.
- Do not fill the coolant reservoir only with plain water, because this will dilute the coolant concentration.
- Any reduction in the coolant level may indicate a leaking in the cooling system.
- Perform the preventive thermostats maintenance every 30.000 Km.
Warranty
All MTE-THOMSON products are guaranteed for 01(one) year against defects from faulty materials or fabrication. The guarantee is limited to the replacement of the faulty part; we cannot extend the guarantee to cover defects caused by misuse, neglect, accident or wear and tear. We cannot accept liability for consequential loss or damage which is claimed to have resulted from the use of one of our products. More information: www.mte-thomson.com.br